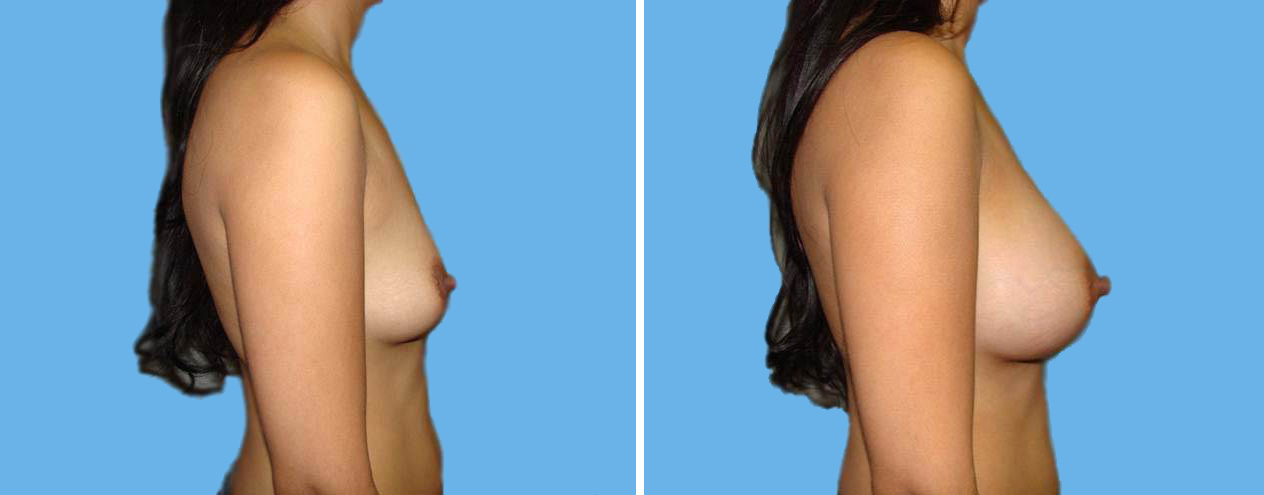
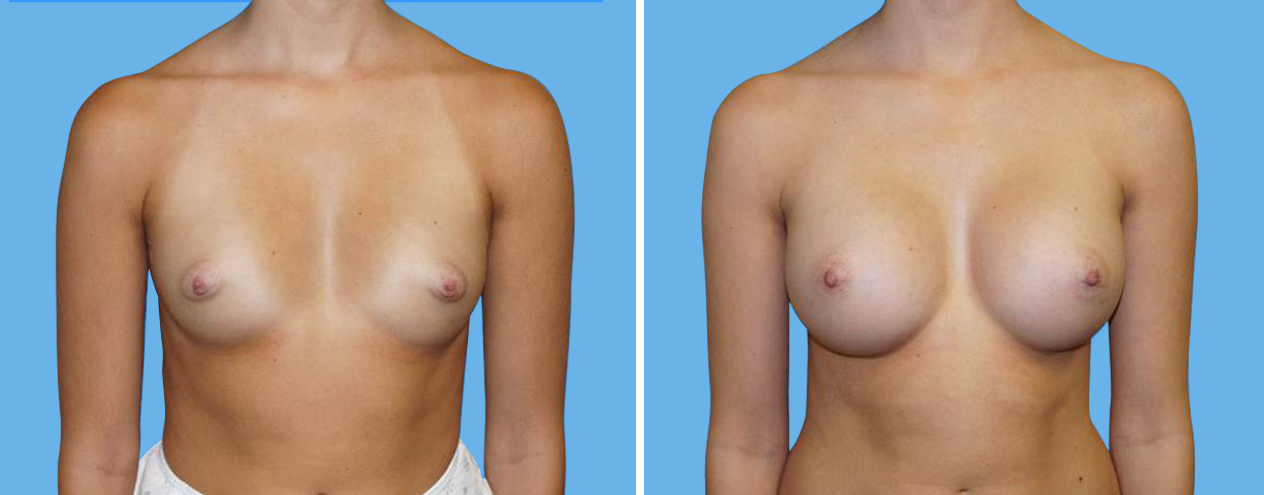
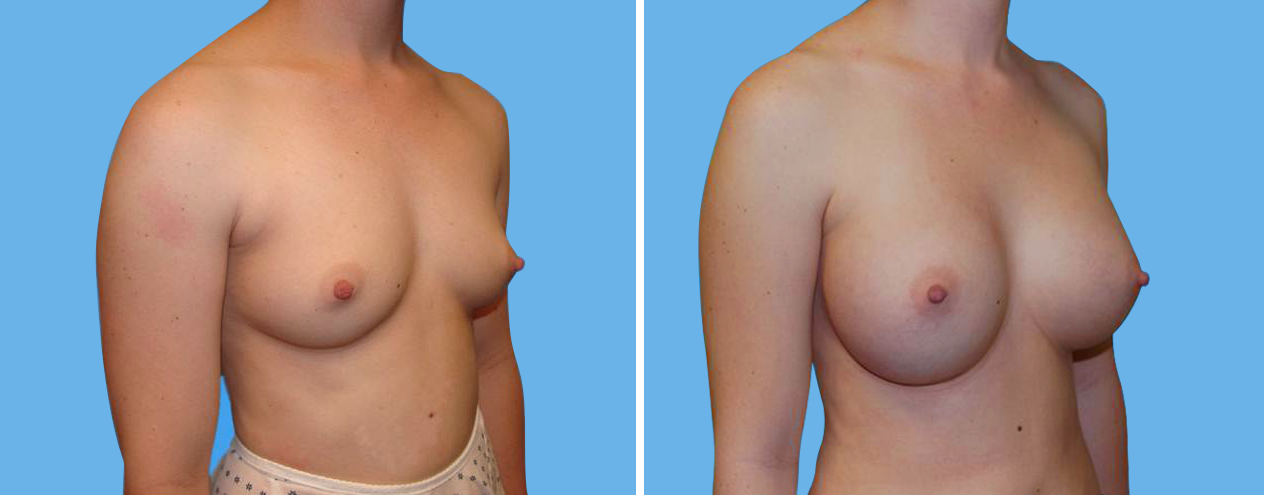
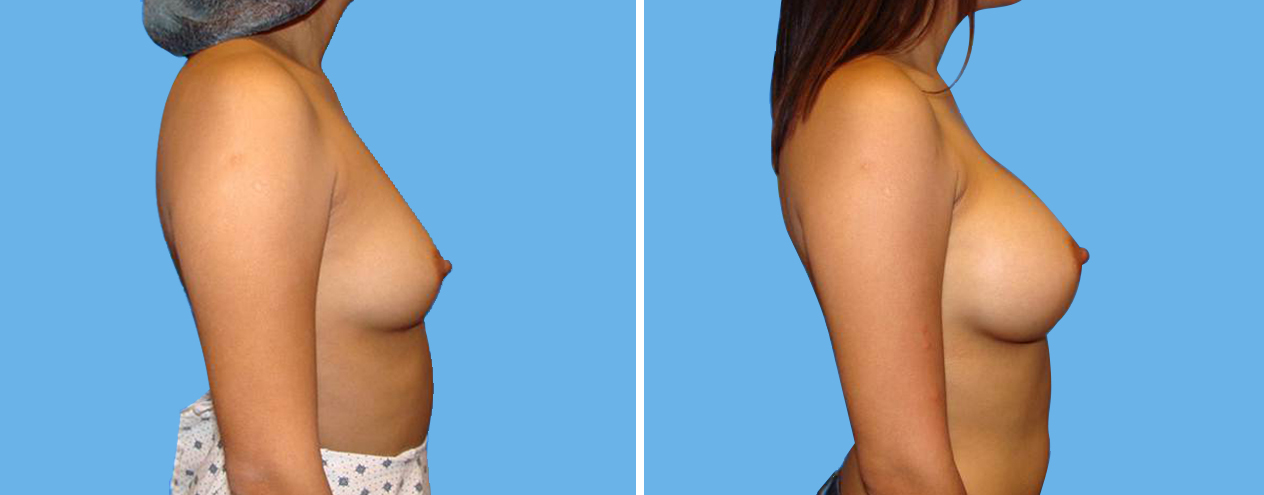
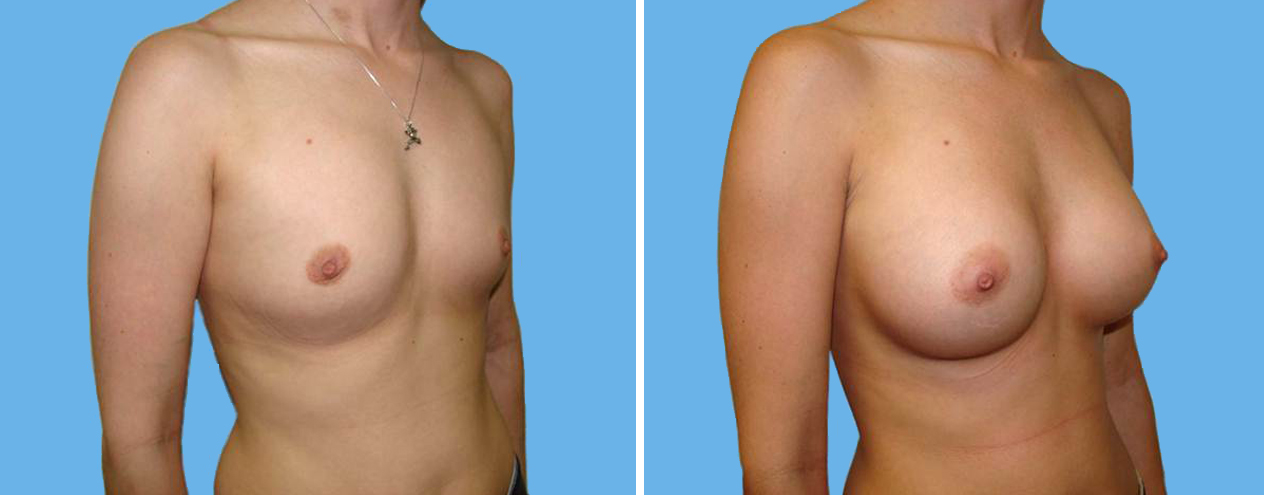
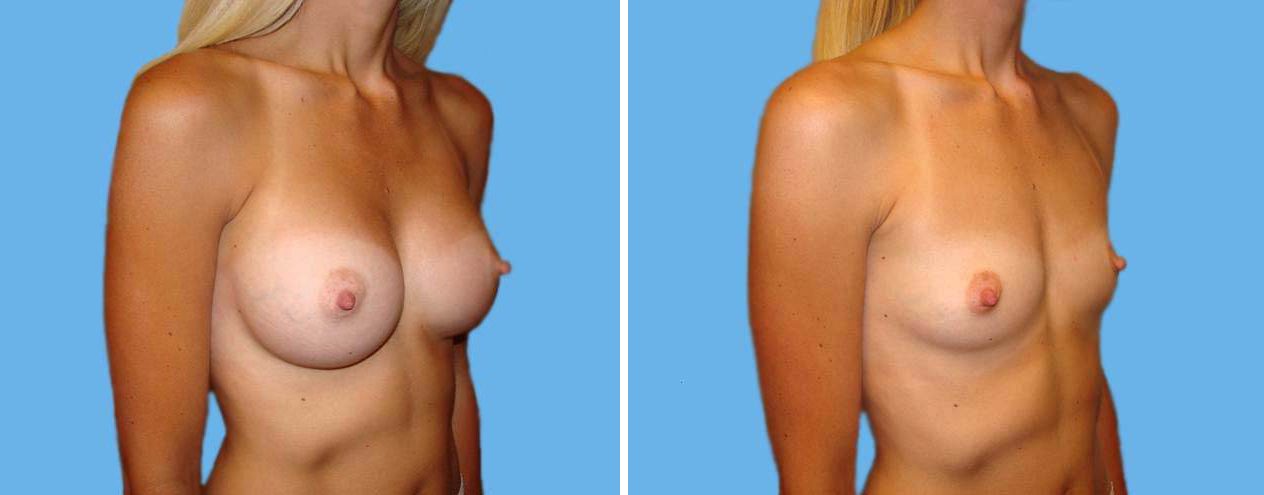
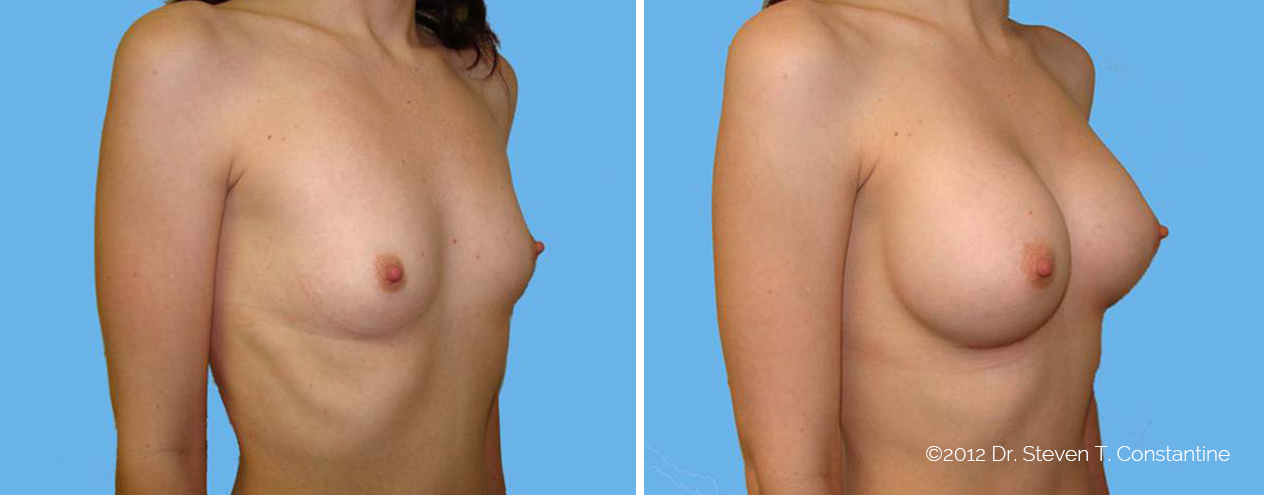
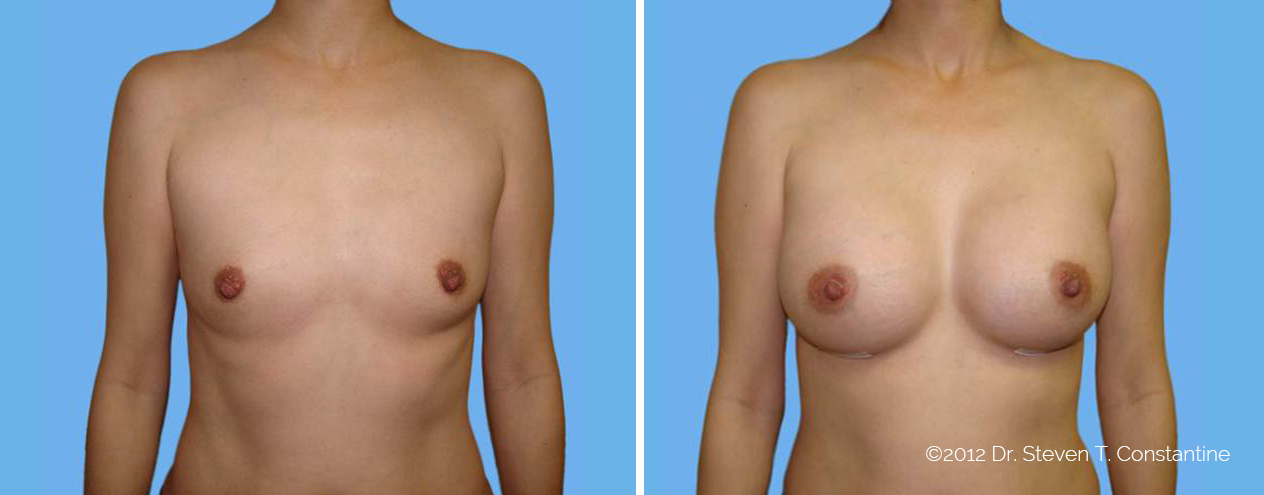
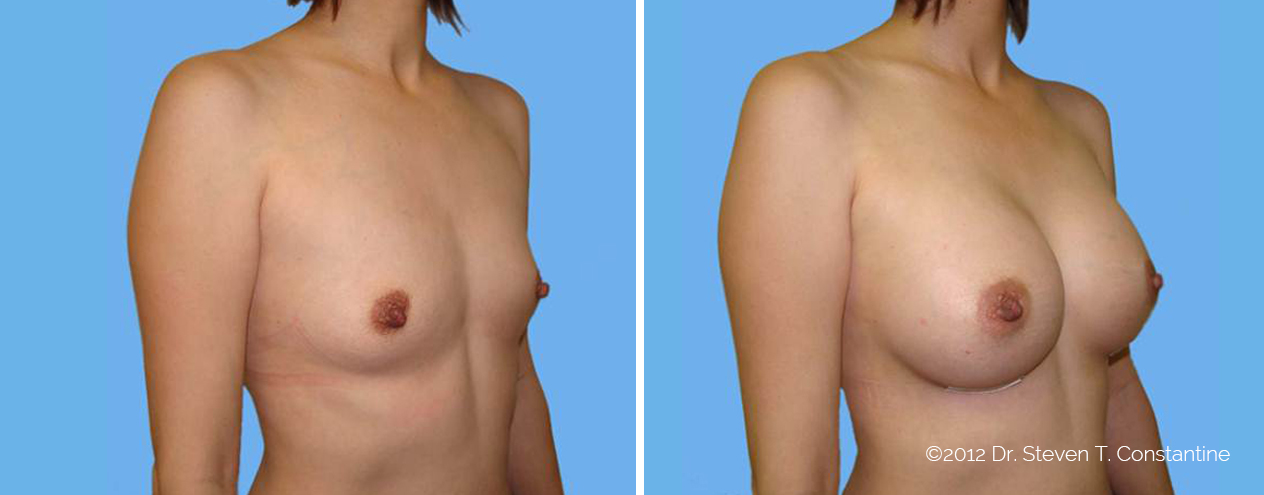
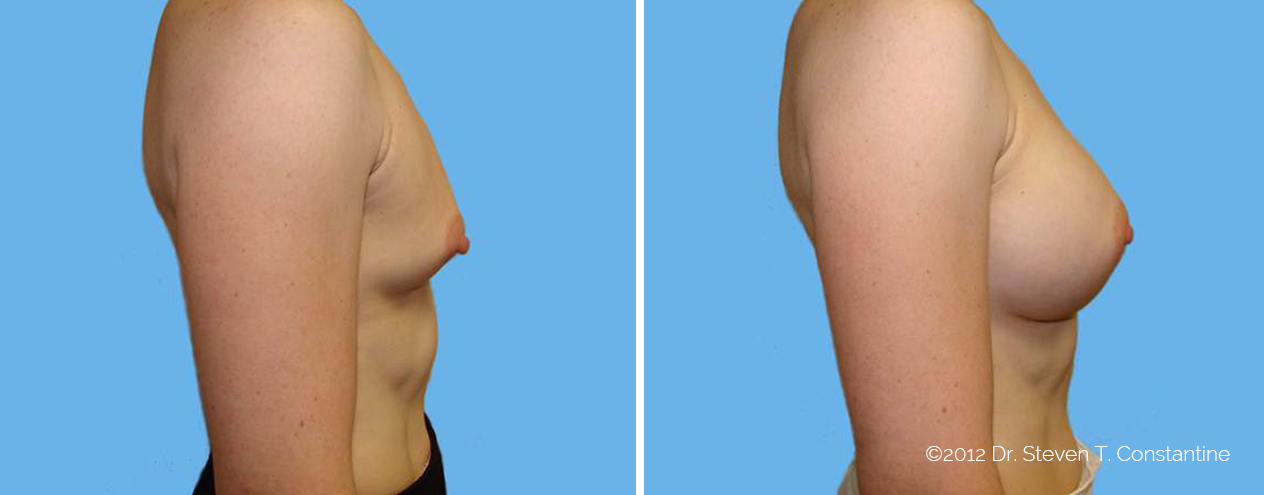
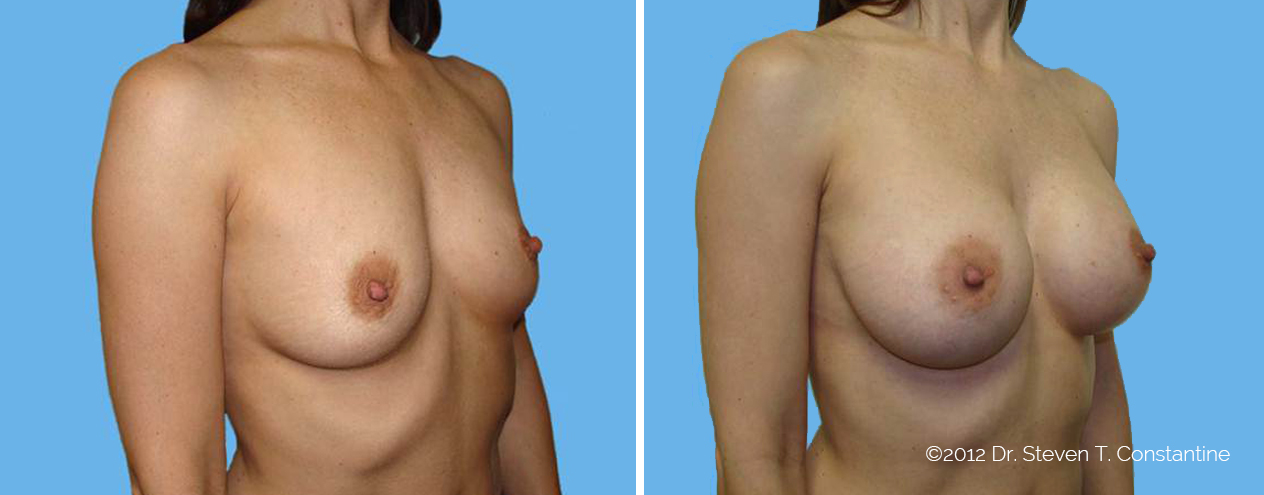
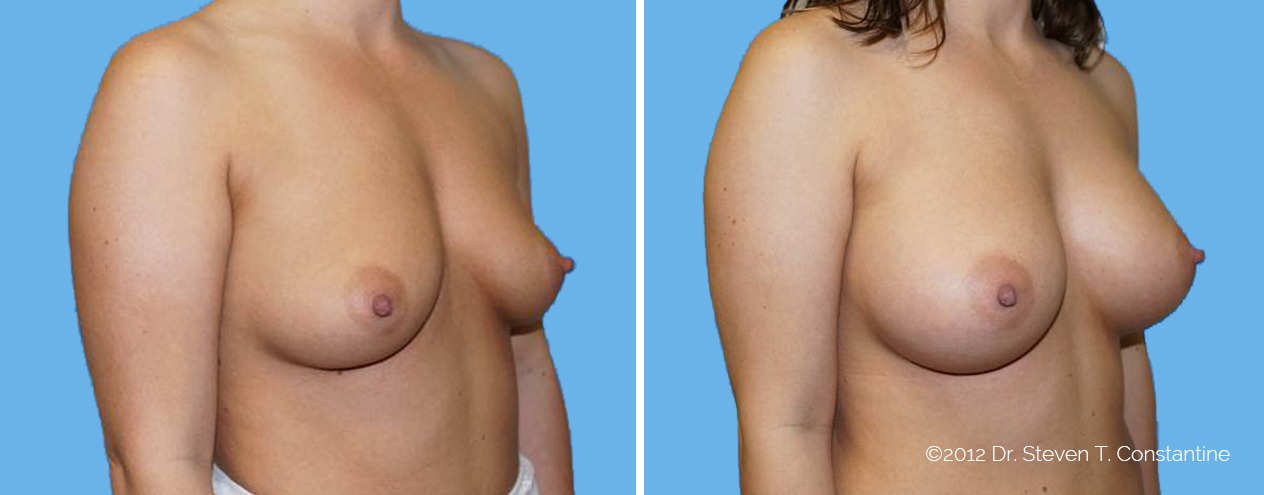
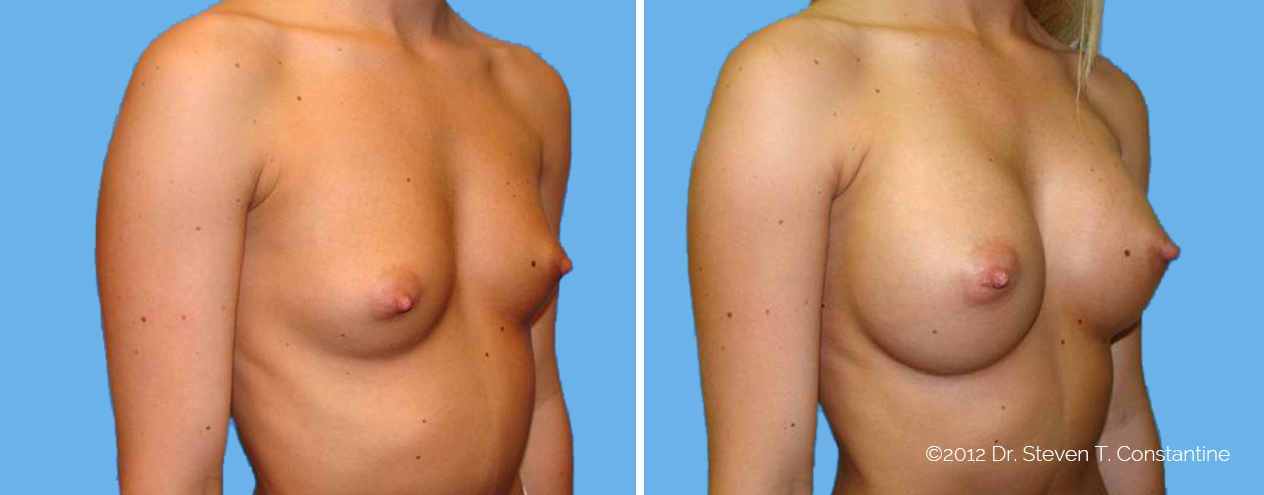
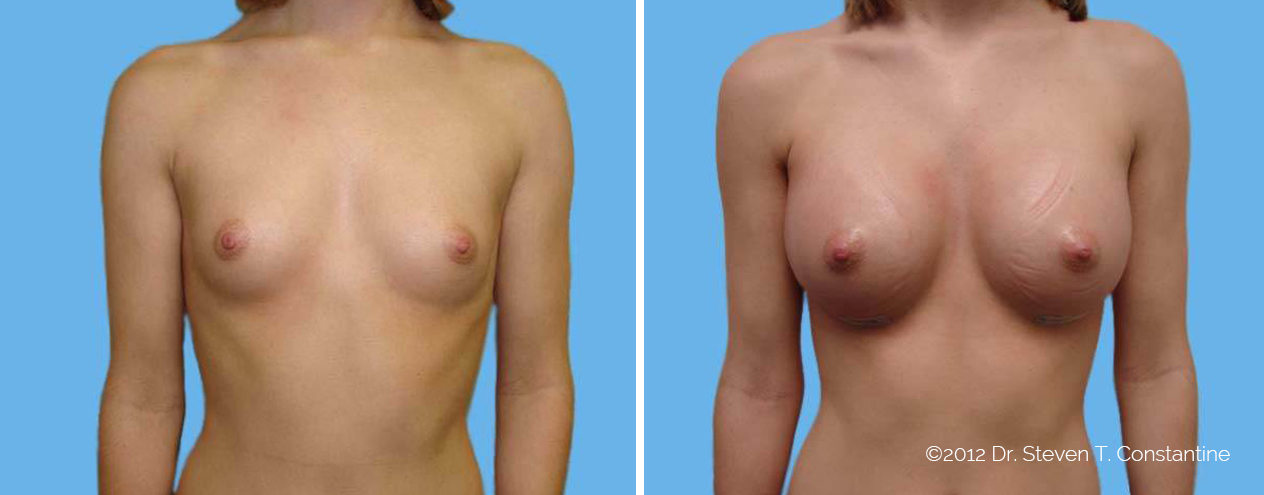
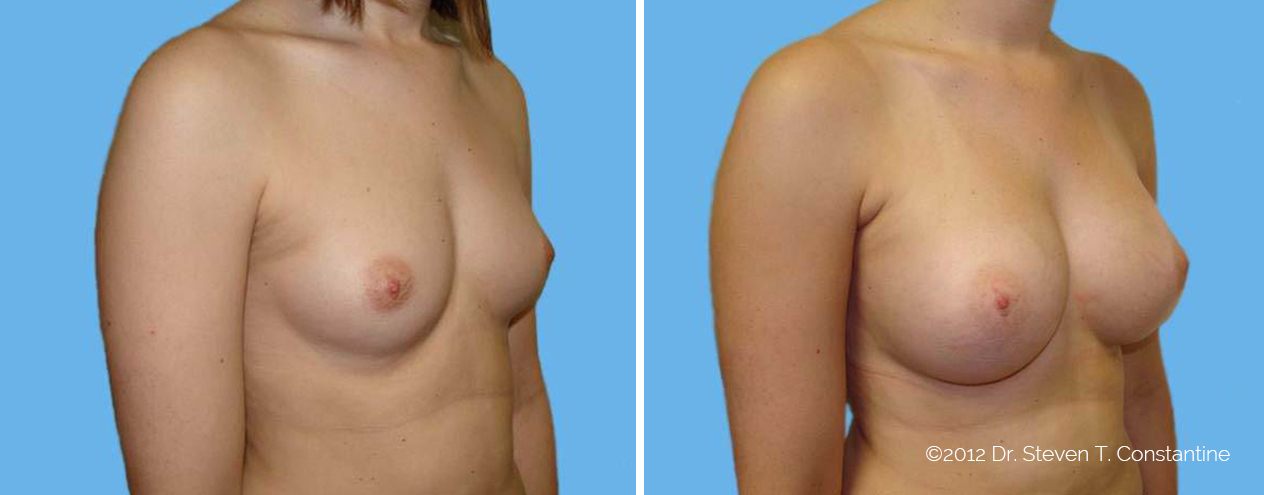
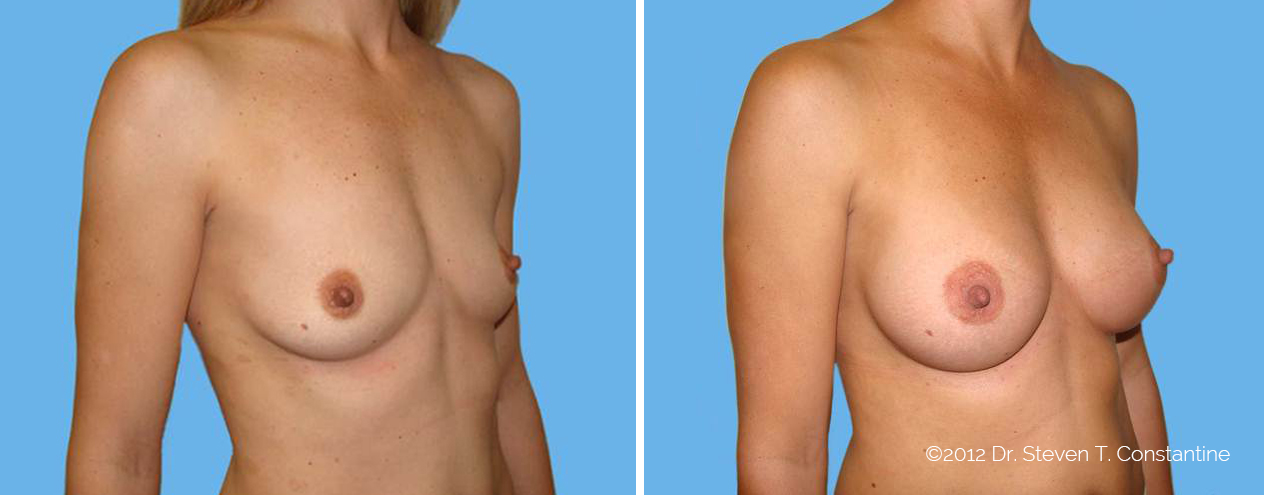
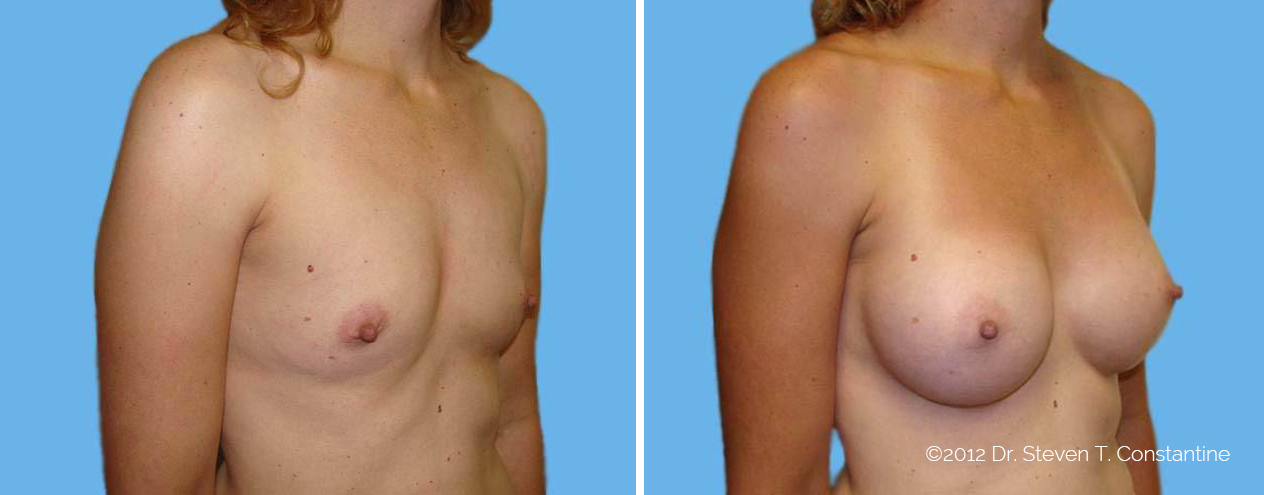
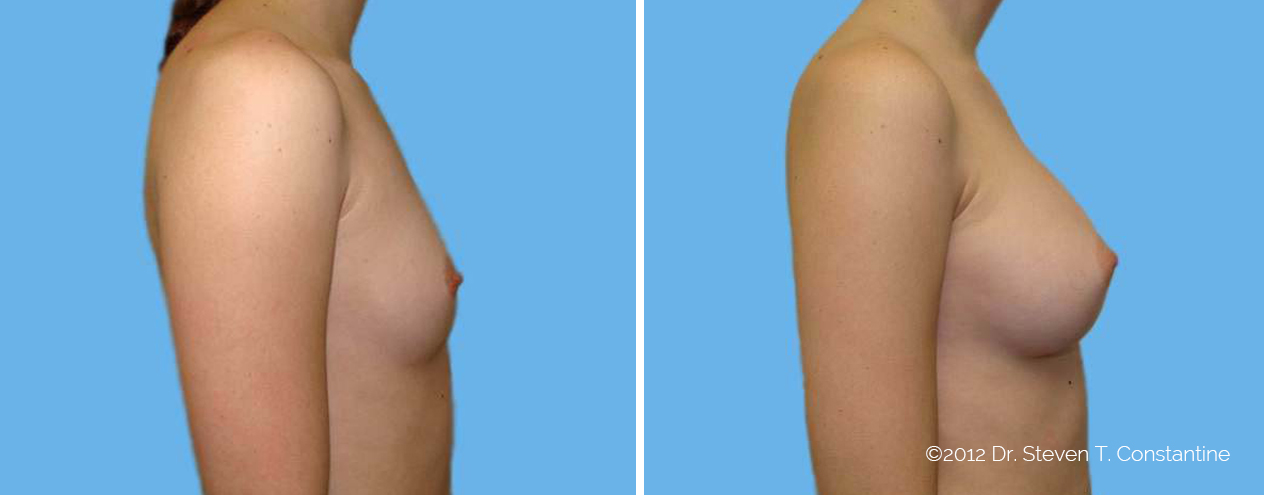
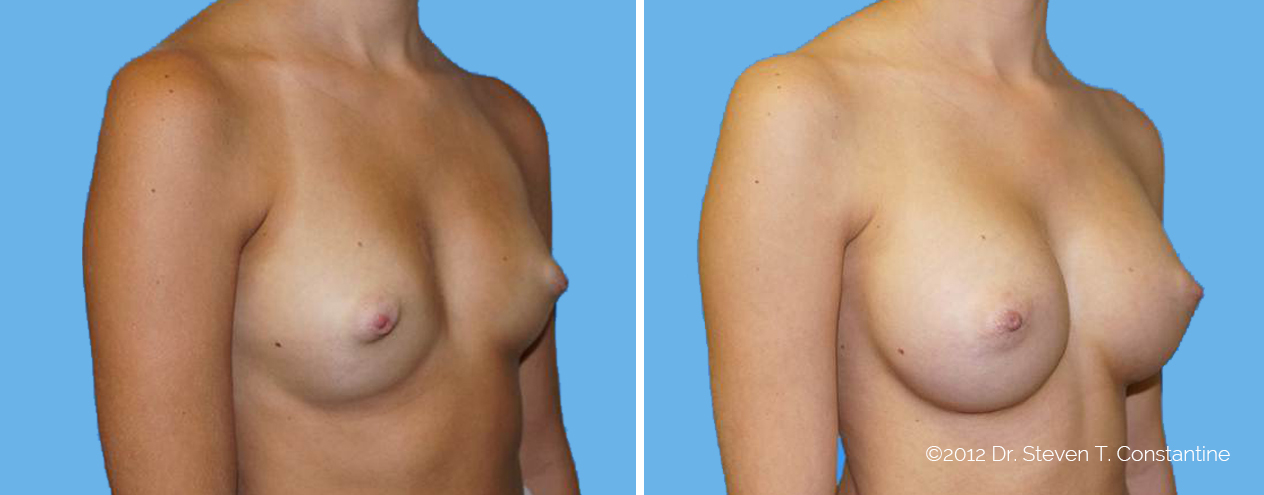
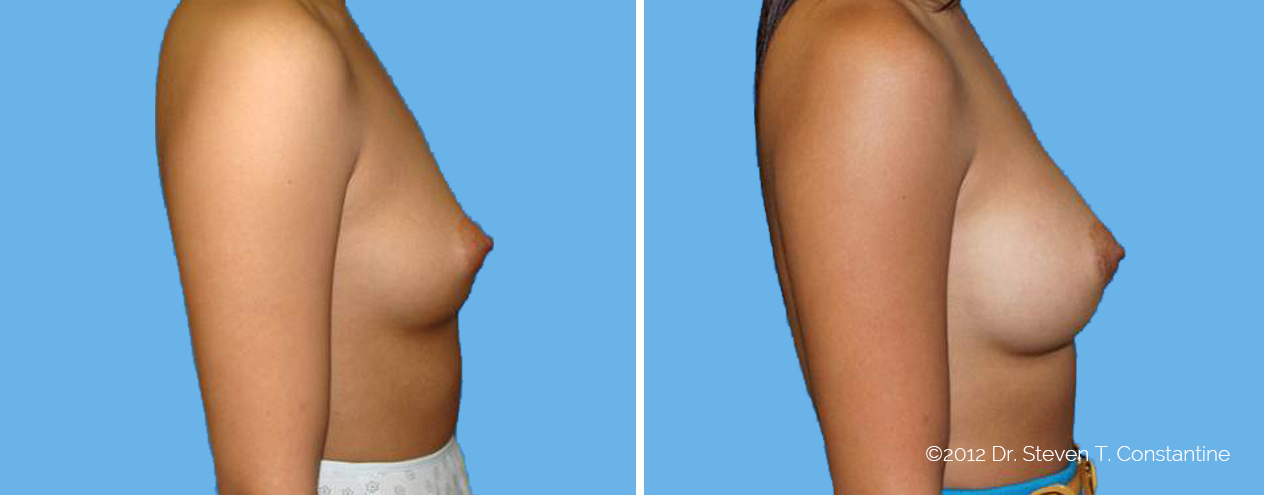
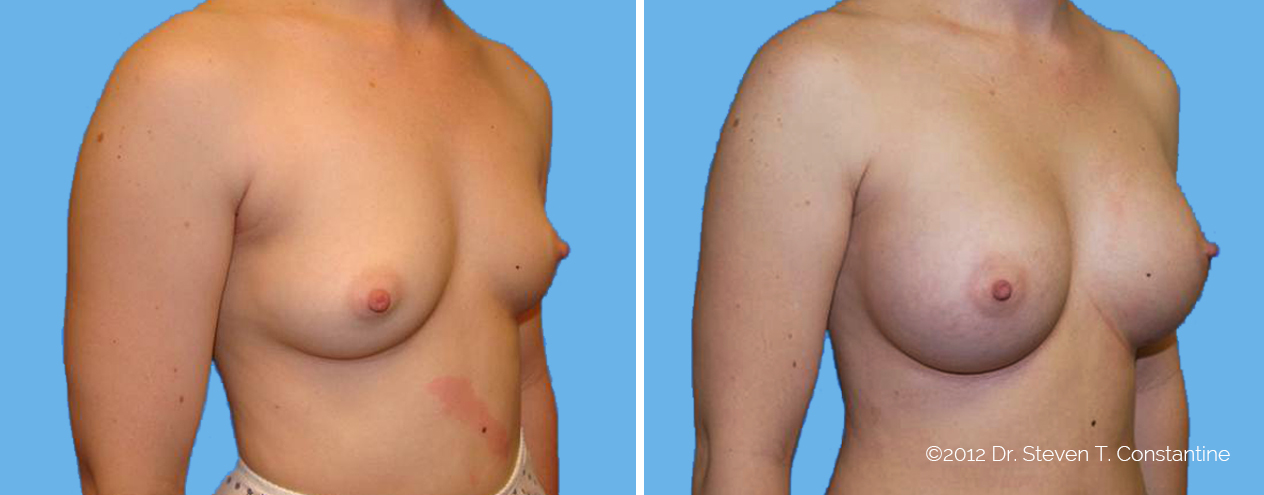
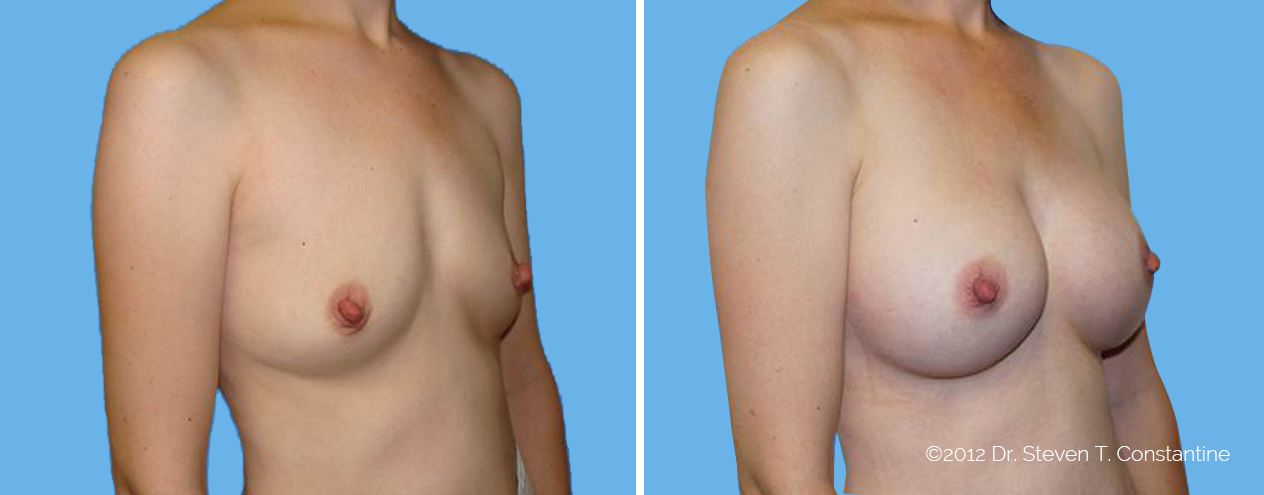
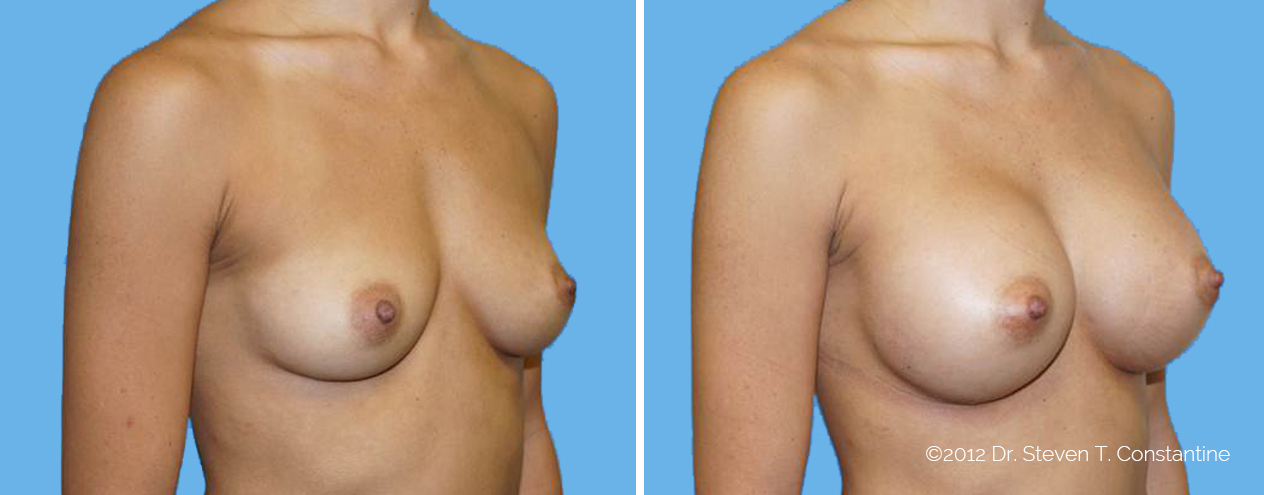
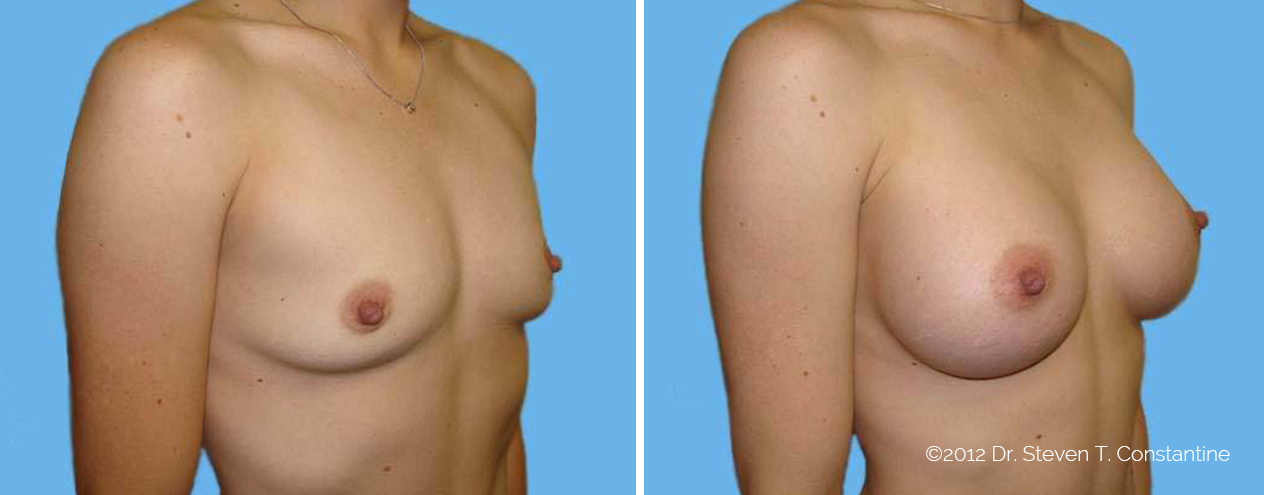
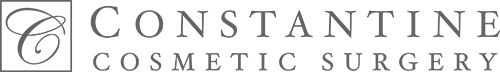Many women would love to have fuller, firmer breasts because they weren't born with the breast size or shape to compliment their body type. Having breasts that give a full, feminine curve to a woman's body can boost self-confidence, and eliminate anxiety about body image. For some of our patients, breast augmentation provides breast volume and shape that has never been present, while for others it restores fullness and balance to their feminine figure that has been lost during weight changes or after pregnancy.
Through an informative process, we will assist you in selecting an implant that provides a natural result that fits your body and enhances your overall beauty. We have found that education is a critical component to a successful outcome. Our patients' experiences are less stressful and more predictable as they become aware of the options and choices available to them and arrive at a decision under the thoughtful guidance of one of our doctors.
Silicone Breast Implants
Silicone breast implants were first popularized in the 1960's. Controversy in the early 1990's led to widespread fear about the possibility of silicone breast implants causing autoimmune diseases in women. Extensive studies since then have showed no evidence that silicone breast implants have any relationship to breast cancer, autoimmune disease or any other systemic illnesses in patients. Specifically, patients with breast implants have no higher incidence of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma or lupus, in comparison with the general population.
The Food & Drug Administration approved the use of the third generation silicone gel implants in November of 2006 for women 22 years of age and older. These implants are not filled with liquid silicone, but rather a cohesive silicone gel.
The increased safety of the cohesive gel implants led to the FDA's approval of these implants for cosmetic use. Saline implants are FDA approved for breast augmentation in women 18 years of age and older. The FDA set the age of approved use higher for silicone gel implants to ensure that a woman is emotionally mature enough and fully understands the risks of these implants.
There is no perfect breast implant and both the saline and silicone gel breast implants have advantages and disadvantages. The silicone gel implants feel softer and more natural, have less chance of rippling, but are more expensive and have a higher chance of developing tightening of the scar tissue around the implant known as capsule contracture.
The manufacturers of silicone gel implants (Mentor and Allergan) recommend that you get an MRI after 3 years and then every 2 years thereafter to ensure that your implants are not leaking. Insurance will likely not cover the cost for an MRI. The manufacturers also warn that your insurance carrier may increase your health premiums or decline coverage if you have silicone gel implants.
Saline Breast Implants
Saline breast implants are very safe and if they become damaged or deflate, your body will absorb the water. Saline implants are more prone to rippling and feel less natural than silicone. We will review the implants with you at your consultation and help you to decide which implant is best suited for you.
Our experience suggests to us that there is approximately an annual 1% risk of leakage from saline implants. The FDA clinical trials for silicone gel implants suggest a leakage rate of 8-15% over the course of 10 years. Replacement is generally a relatively simple operation. Additional cost is involved, but most implant companies offer warranties that help offset a small portion of the fees for up to 5 to 10 years.
Positioning of the Breast Implant
 Implants can be placed beneath the pectoral muscle of the chest wall or directly behind the breast tissue. Most patients will have their implants placed behind the chest muscle unless there are anatomic considerations that warrant the implants being placed directly behind the breast tissue. Some studies have suggested that implants placed behind your chest muscle have a lower risk of forming capsular contracture (scar tissue that hardens around the implant) and interfere less with breast examination by mammogram than if the implant is placed directly behind the breast tissue. Placement behind the muscle does lead to more muscular discomfort in the initial days after surgery than placement directly under the breast.
Implants can be placed beneath the pectoral muscle of the chest wall or directly behind the breast tissue. Most patients will have their implants placed behind the chest muscle unless there are anatomic considerations that warrant the implants being placed directly behind the breast tissue. Some studies have suggested that implants placed behind your chest muscle have a lower risk of forming capsular contracture (scar tissue that hardens around the implant) and interfere less with breast examination by mammogram than if the implant is placed directly behind the breast tissue. Placement behind the muscle does lead to more muscular discomfort in the initial days after surgery than placement directly under the breast.
Other Areas of Interest